 bicycle
bicycle
Manual
Contents
1. Requirements
bicycle requirements to run it locally are:
- Operating system: Linux/OSX.
- Java 1.8 or higher.
- One of the following aligners:
- bowtie1 0.12.7 or higher and 1.0.0 or lower.
- bowtie2 aligner 2.3.2 or higher.
- samtools 0.1.8 or higher.
Alternatively, there is a bicycle Docker image at Dockerhub which includes the latest version and all dependencies.
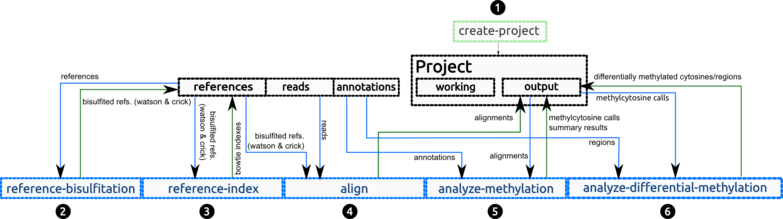
2. bicycle pipeline
bicycle is based on 6 main commands, where the temporal data and results are stored in a project. Output files are placed in the ./output directory inside the project's directory
The commands are:
- Create project. A project is simply a new directory with a configuration file poiting to the references, reads, samtools and bowtie directories.
- Reference bisulfitation. Creation of the bisulfited references (both Watson and Crick). By default, the generated references are placed in the references directory, in order to reuse this reference in several methylation projects.
- Reference index. Build bowtie indexes of the bisulfited references. As before, the generated indexes are placed in the references directory.
- Align. Align all bisulfited reads against the bisulfited references and place the alignments in the "output" subdirectory of the project.
- Analyze methylation. Methylation level analysis and methylcytosines calling.
- Analyze differential methylation. Differential methylation analysis.
By running bicycle, a list of the available commands is shown:
usage: bicycle <command> [options]
where <command> is one of:
create-project
Creates a new directory where working data and results will be stored
reference-bisulfitation
Performs reference in-silico bisulfitation (CtoT and GtoA)
reference-index
Tells Bowtie to build indexes for both references, CtoT and GtoA
align
Aligns with Bowtie against both references using multiple bowties (CtoT and GtoA)
analyze-methylation
Analyzes methylation levels over the Sam files with the GATK-based walker
analyze-differential-methylation
Analyzes differential methylation for treatment-control samples at base or region level
Depending on the command you have chosen, you will have additional options. This section provides a detailed description of each command as well as the required input files and expected results.
2.1.1 create-project
usage: bicycle create-project -p <project-directory> -r <reference-directory> -f <reads-directory> [-b <bowtie-directory>] [-b2 <bowtie2-directory>] [-s <samtools-directory>] [-n] [-m <paired-mate1-regexp>]
--project-directory/-p
directory where files will be stored
--reference-directory/-r
directory with reference genomes (fasta files)
--reads-directory/-f
directory with reads samples (directories with fastq files). One directory per sample
--bowtie-directory/-b
directory where bowtie v1.x.x aligner is installed. If not specified and you will use bowtie 1 during alignment, bowtie 1 is expected to be in PATH
--bowtie2-directory/-b2
directory where bowtie v2.x.x aligner is installed. If not specified and you will use bowtie 2 during alignment, bowtie 2 is expected to be in PATH
--samtools-directory/-s
directory where samtools are installed. If not specified, samtools is expected to be in PATH
--non-directional/-n
bs-seq was made in non-directional protocol
--paired-mate1-regexp/-m
Enable paired-end mode. The value is a regular expression which only can be found inside the mate 1 fastq file names. For example: _1.fastq
Input files
- A directory with reference genomes (FASTA format, with .fa extension). All .fa files will be considered.
-
A directory with sequenced reads (FASTQ format, with .fastq extension). Each FASTQ file will be considered a sample.
- Note: if you have multiple FASTQ files for the same sample, you have to organize each sample in a subdirectory inside the reads directory.
Output files
- A bicycle project directory.
2.1.2 reference-bisulfitation
usage: bicycle reference-bisulfitation -p <project-directory> [-w]
--project-directory/-p
project directory. Use command create-project to create a new project
--on-working-dir/-w
generate output files on working dir (by default, bisulfited reference will be placed together with reference files)
Input files
- A bicycle project directory.
Output files
- Watson and Crick bisulfited reference genomes in the reference genomes directory. If --on-working-dir option is used, they are placed in the bicycle project directory.
2.1.3 reference-index
usage: bicycle reference-index -p <project-directory> [-v <bowtie-version>] [-t <bowtie2-t>]
--project-directory/-p
project directory. Use command create-project to create a new project
--bowtie-version/-v
bowtie version to use (valid options are 1 or 2) (default: 2)
--bowtie2-t/-t
number of threads (only for bowtie2) (default: 2)
Input files
- A bicycle project directory.
Output files
- Bisulfited reference genomes indexes in the same directory that bisulfited reference genomes are located.
2.1.4 align
usage: bicycle align -p <project-directory> [-t <threads>] [-b] [-v <bowtie-version>] [-e <bowtie-maqerr>] [-l <bowtie-seedlen>] [-n <bowtie-seedmms>] [-I <bowtie-I>] [-X <bowtie-X>] [-c <bowtie-chunkmbs>] [-q <bowtie-quals>] [-o] [-D <bowtie2-D>] [-R <bowtie2-R>] [-L2 <bowtie2-L>] [-f <bowtie2-i-func>] [-N2 <bowtie2-N>] [-I2 <bowtie2-I>] [-X2 <bowtie2-X>] [-q2 <bowtie2-quals>] [-sm <bowtie2-score-min>]
--project-directory/-p
project directory. Use command create-project to create a new project
--threads/-t
number of threads per sample and ref alignment (default: 4)
--skip-unconverted-barcodes/-b
skip reads with unconverted barcodes. The barcode should be on the name of the read files and delimited by '_' and '-'. For example, a valid reads file name would be: AML_s_8_TGtATT-reads.fastq, so the barcode is TGtATT
--bowtie-version/-v
bowtie version to use (valid options are 1 or 2) (default: 2)
--bowtie-maqerr/-e
Maximum permitted total of quality values at all mismatched read positions throughout the entire alignment, not just in the "seed" (default: 140)
--bowtie-seedlen/-l
The "seed length"; i.e., the number of bases on the high-quality end of the read to which the -n ceiling applies. The lowest permitted setting is 5 and the default is 28. bowtie is faster for larger values of -l. (default: 20)
--bowtie-seedmms/-n
Maximum number of mismatches permitted in the "seed", i.e. the first L base pairs of the read (where L is set with -l/--bowtie-seedlen). This may be 0, 1, 2 or 3 (default: 0)
--bowtie-I/-I
The minimum insert size for valid paired-end alignments (paired-end projects only) (default: 0)
--bowtie-X/-X
The maximum insert size for valid paired-end alignments (paired-end projects only) (default: 250)
--bowtie-chunkmbs/-c
The number of megabytes of memory a given thread is given to store path descriptors (default: 64)
--bowtie-quals/-q
How qualities will be treated. Valid values are: solexa1.3, solexa, phred33, phred64, integer (default: solexa1.3)
--bowtie2-local/-o
Enables --local mode (by default the --end-to-end mode is used). In this mode, Bowtie 2 does not require that the entire read align from one end to the other. Rather, some characters may be omitted ("soft clipped") from the ends in order to achieve the greatest possible alignment score
--bowtie2-D/-D
How many consecutive seed extension attempts can "fail" before Bowtie 2 moves on, using the alignments found so far. A seed extension "fails" if it does not yield a new best or a new second-best alignment (default: 15)
--bowtie2-R/-R
Maximum number of times Bowtie 2 will "re-seed" reads with repetitive seeds. When "re-seeding," Bowtie 2 simply chooses a new set of reads (same length, same number of mismatches allowed) at different offsets and searches for more alignments. A read is considered to have repetitive seeds if the total number of seed hits divided by the number of seeds that aligned at least once is greater than 300 (default: 2)
--bowtie2-L/-L2
Sets the length of the seed substrings to align during multiseed alignment. Smaller values make alignment slower but more sensitive (default: 20)
--bowtie2-i-func/-f
Sets a function governing the interval between seed substrings to use during multiseed alignment. See bowtie2 manual for details. The default in --end-to-end mode is S,1,1.15 and S,1,0.75 in --local mode
--bowtie2-N/-N2
Sets the number of mismatches to allowed in a seed alignment during multiseed alignment. Can be set to 0 or 1. Setting this higher makes alignment slower (often much slower) but increases sensitivity. Default: 0 (default: 0)
--bowtie2-I/-I2
The minimum fragment length for valid paired-end alignments (paired-end projects only) (default: 0)
--bowtie2-X/-X2
The maximum fragment length for valid paired-end alignments (paired-end projects only) (default: 500)
--bowtie2-quals/-q2
How qualities will be treated. Valid values are: solexa, phred33, phred64, int (default: phred64)
--bowtie2-score-min/-sm
Sets a function governing the minimum alignment score needed for an alignment to be considered "valid" (i.e. good enough to report). This is a function of read length. For instance, specifying L,0,-0.6 sets the minimum-score function f to f(x) = 0 + -0.6 * x, where x is the read length. See bowtie2 manual for details. The default in --end-to-end mode is L,-0.6,-0.6 and in --local mode is G,20,8.
Input files
- A bicycle project directory.
Output files
- SAM files with read alignments, stored in the output directory of the bicycle project directory.
2.1.5 analyze-methylation
usage: bicycle analyze-methylation -p <project-directory> [-n <threads>] [-r] [-a] [-o] [-t <trim-reads>] [-d <min-depth>] [-f <fdr>] [-e <error-mode>] [-b <annotate-beds>] [-c] [-g]
--project-directory/-p
project directory. Use command create-project to create a new project
--threads/-n
number of threads to analyze (default: 4)
--remove-uncorrectly-converted/-r
ignore non-correctly bisulfite-converted reads
--remove-ambiguous/-a
ignore reads aligned to both Watson and Crick strands
--only-with-one-alignment/-o
ignore reads with more than one possible alignment
--trim-reads/-t
Trim reads to the <t> mismatch. 0 means no trim (default: 4)
--min-depth/-d
Ignore positions with less than <d> reads (default: 1)
--fdr/-f
FDR threshold (default: 0.01)
--error-mode/-e
Error rate computation mode. Valid options are: from_control_genome=<control_genome_name>, from_barcodes, FIXED=<watson_error_rate,crick_error_rate> (default: FIXED=0.01,0.01)
--annotate-beds/-b
Comma-separated (with no spaces) list of BED files to annotate cytosines
--remove-clonal/-c
Remove clonal reads
--correct non-CG to CG/-g
Correct non-CG
Input files
- A bicycle project directory.
Output files
-
<sample-name>_<reference-name>.summary. Contains the final methylation analysis results, which include:
- Experiment parameters
- Error computation results
- p-value cutoffs for FDR adjustment
-
Methylation details:
- Methylcytosines calling. For each cytosine, the methylation level is tested for significance, based on bisulfite error. A cytosine whose p-value is less than the FDR cutoff is called as a methylcytosine. Here you will find:
- Methylcytosines distribution across contexts
- Per-context frequencies of methylcytosines
- Methylation levels. Per-context frequency of methylated reads at each reference cytosine
- Methylcytosines calling. For each cytosine, the methylation level is tested for significance, based on bisulfite error. A cytosine whose p-value is less than the FDR cutoff is called as a methylcytosine. Here you will find:
====METHYLATION RESULTS======================================================= File: SRR2052496_hg19.fa.summary Date: Fri Oct 27 12:33:18 UTC 2017 ====ANALYSIS PARAMETERS======================================================= Correct non-CG: false Filters: Mapped reads processed: 2354968 remove ambiguous reads: true (33 removed (0.00%)) remove with more than one alignment: true (94 removed (0.00%)) remove non-correctly bisulfite-converted reads: false trim to 'x' mismatch: true x=4 98132 trimmed (4.17%) remove clonal reads: false FDR threshold: 0.01 ====ERROR ESTIMATION AND SIGNIFICANCE ADJUSTMENTS============================= Error rates (fixed): WATSON = {CG = 0.01, CHG = 0.01, CHH = 0.01} CRICK = {CG = 0.01, CHG = 0.01, CHH = 0.01} p-value cutoffs: {WATSON={CHG=0.0031645569620253173, CG=0.07999999999999997, CHH=0.0016956521739130434}, CRICK={CHG=0.0014285714285714286, CG=0.03, CHH=6.666666666666666E-4}} ====METHYLATION ANALYSIS RESULTS============================================== ---- GLOBAL -------- Called methylcytosines (pval<cutoff) total: 102/453 (0.2251655629139073) per context called methylcytosines: CG:0.3431372549019608 CHG:0.2549019607843137 CHH:0.4019607843137255 CG called methylcytosines: 35/40 (0.875) CHG called methylcytosines: 26/112 (0.23214285714285715) CHH called methylcytosines: 41/301 (0.1362126245847176) Methylation Levels: CG: 3773852/8454899 (0.4463509262499765) CHG: 725033/34051297 (0.02129237544167554) CHH: 1110237/52260949 (0.02124410331699105) non-CG corrections: 0 ---- WATSON -------- Called methylcytosines (pval<cutoff) total: 96/409 (0.23471882640586797) per context called methylcytosines: CG:0.3333333333333333 CHG:0.2604166666666667 CHH:0.40625 CG called methylcytosines: 32/36 (0.8888888888888888) CHG called methylcytosines: 25/104 (0.2403846153846154) CHH called methylcytosines: 39/269 (0.1449814126394052) Methylation Levels: CG: 3773837/8454878 (0.44635026076071116) CHG: 725028/34051138 (0.02129232802733348) CHH: 1110183/52260298 (0.021243334662959634) non-CG corrections: 0 ---- CRICK -------- Called methylcytosines (pval<cutoff) total: 6/44 (0.13636363636363635) per context called methylcytosines: CG:0.5 CHG:0.16666666666666666 CHH:0.3333333333333333 CG called methylcytosines: 3/4 (0.75) CHG called methylcytosines: 1/8 (0.125) CHH called methylcytosines: 2/32 (0.0625) Methylation Levels: CG: 15/21 (0.7142857142857143) CHG: 5/159 (0.031446540880503145) CHH: 54/651 (0.08294930875576037) non-CG corrections: 0 Cut-off computation details: WATSON Iteration 1, M: [1.0, 1.0, 1.0] %mC: [88.88888888888889, 25.961538461538463, 22.676579925650557] need Adjust: [true, true, true] Iteration 2, M: [0.07999999999999997, 0.003506493506493507, 0.0029326923076923076] %mC: [88.88888888888889, 24.03846153846154, 14.49814126394052] need Adjust: [false, true, true] Iteration 3, M: [0.07999999999999997, 0.0031645569620253173, 0.0016956521739130434] %mC: [88.88888888888889, 24.03846153846154, 14.49814126394052] need Adjust: [false, false, false] Finished p-value adjust. Result [0.07999999999999997, 0.0031645569620253173, 0.0016956521739130434] CRICK Iteration 1, M: [1.0, 1.0, 1.0] %mC: [75.0, 12.5, 9.375] need Adjust: [true, true, true] Iteration 2, M: [0.03, 0.0014285714285714286, 0.0010344827586206897] %mC: [75.0, 12.5, 6.25] need Adjust: [false, false, true] Iteration 3, M: [0.03, 0.0014285714285714286, 6.666666666666666E-4] %mC: [75.0, 12.5, 6.25] need Adjust: [false, false, false] Finished p-value adjust. Result [0.03, 0.0014285714285714286, 6.666666666666666E-4] -
<sample-name>_<reference-name>.methylcytosines. This file contains a line for each reference cytosine. The methylation level () is given as well as an FDR-adjusted significance value is reported for this methylation level. Columns are:
- SEQUENCE and POS
- STRAND: Watson or Crick
- CONTEXT: CG, CHG or CHH
- DEPTH: number of reads at the position
- CT.DEPTH: number of reads with Cytosine (Guanine in Crick) or Thymine (Adenine in Crick)
- CYTOSINE.COUNT: number of reads with Cytosine (Guanine in Crick)
- BETA.SCORE: for methylation level.
- PILEUP: readed bases at the position
- PVAL: Probability of the being greater than the observed assuming the bisulfite conversion error rate
- CORRECTED_FROM_NON_CG: If the context is a CG corrected from a non-CG
- ADDED BY CORRECTION: If the context is a CG added by the correction in the opposite strand
- BED_FILE_#: If bed files are used for annotation, an additional column with each bed file will be added. The values are those intervals on the bed file that overlaps in the position
- STATUS: If the cytosine has been called as methylcytosine, that is, it can be statistical considered as methylated (its p-value is less than the computed cutoff for FDR adjustment). Values are: METHYLATED or UNMETHYLATED
#SEQUENCE POS STRAND CONTEXT DEPTH CT.DEPTH CYTOSINE.COUNT BETA.SCORE PILEUP PVAL CORRECTED_FROM_NON_CG ADDED_BY_CORRECTION STATUS chr1 3002506 CRICK CHH 5 5 0 0.0 AAAAA 1.0 false false UNMETHYLATED chr1 3002507 WATSON CHH 6 6 0 0.0 TTTTTT 1.0 false false UNMETHYLATED chr1 3002511 WATSON CHG 7 7 0 0.0 TTTTTTT 1.0 false false UNMETHYLATED chr1 3002513 CRICK CHG 5 5 0 0.0 AAAAA 1.0 false false UNMETHYLATED chr1 3002514 WATSON CHH 7 7 0 0.0 TTTTTTT 1.0 false false UNMETHYLATED chr1 3002515 WATSON CHH 7 7 0 0.0 TTTTTTT 1.0 false false UNMETHYLATED chr1 3002518 CRICK CHH 5 5 0 0.0 AAAAA 1.0 false false UNMETHYLATED chr1 3002519 WATSON CHH 7 7 0 0.0 TTTTTTT 1.0 false false UNMETHYLATED chr1 3002522 WATSON CHG 7 7 1 0.1429 TTCTTTT 0.007 false false UNMETHYLATED chr1 3002524 CRICK CHG 5 5 1 0.20 AGAAA 0.005 false false UNMETHYLATED chr1 3002526 WATSON CHG 7 7 1 0.1429 TTTTCTT 0.007 false false UNMETHYLATED chr1 3002528 CRICK CHG 4 4 0 0.0 AAAA 1.0 false false UNMETHYLATED chr1 3002529 WATSON CHH 7 7 0 0.0 TTTTTTT 1.0 false false UNMETHYLATED chr1 3002530 WATSON CHH 7 7 2 0.2857 TTTTCTC 2.18E-5 false false METHYLATED
-
<sample-name>_<reference-name>.methylcytosines.vcf. The same info as the previous file, but in VCF (you can see the comment lines at the start of the file for more info), useful to see it in UCSC. The methylation level is reported in the INFO column, under the BS attribute. The methylcytosine calling is provided in the ALT column, where there is a '.' when there is no methylation, 'C', otherwise.
#fileformat=VCFv4.1 ##INFO=<ID=NS,Number=1,Type=Integer,Description="Number of Samples With Data"> ##INFO=<ID=DP,Number=1,Type=Integer,Description="Total Depth"> ##INFO=<ID=CTDP,Number=1,Type=Integer,Description="CorT Depth"> ##INFO=<ID=CD,Number=1,Type=Integer,Description="Cytosine Depth"> ##INFO=<ID=BS,Number=1,Type=Float,Description="Beta Score"> ##INFO=<ID=PU,Number=1,Type=Float,Description="Readed bases at this position"> ##INFO=<ID=CO,Number=1,Type=Flag,Description="Corrected, i.e., this CG is derived from a non-GC to GC correction"> ##INFO=<ID=AC,Number=1,Type=Flag,Description="Added by correction, i.e., this CG is added due to a correction from non-CG to CG in the opposite strand"> ##INFO=<ID=STR,Number=1,Type=String,Description="Strand Aligment"> #CHROM POS ID REF ALT QUAL FILTER INFO chr1 3002506 CHH C . . . NS=1;DP=5;CTDP=5;CD=0;BS=0;PU=AAAAA;STR=-; chr1 3002507 CHH C . . . NS=1;DP=6;CTDP=6;CD=0;BS=0;PU=TTTTTT;STR=+; chr1 3002511 CHG C . . . NS=1;DP=7;CTDP=7;CD=0;BS=0;PU=TTTTTTT;STR=+; chr1 3002513 CHG C . . . NS=1;DP=5;CTDP=5;CD=0;BS=0;PU=AAAAA;STR=-; chr1 3002514 CHH C . . . NS=1;DP=7;CTDP=7;CD=0;BS=0;PU=TTTTTTT;STR=+; chr1 3002515 CHH C . . . NS=1;DP=7;CTDP=7;CD=0;BS=0;PU=TTTTTTT;STR=+; chr1 3002518 CHH C . . . NS=1;DP=5;CTDP=5;CD=0;BS=0;PU=AAAAA;STR=-; chr1 3002519 CHH C . . . NS=1;DP=7;CTDP=7;CD=0;BS=0;PU=TTTTTTT;STR=+; chr1 3002522 CHG C . . . NS=1;DP=7;CTDP=7;CD=1;BS=0.1429;PU=TTCTTTT;STR=+; chr1 3002524 CHG C . . . NS=1;DP=5;CTDP=5;CD=1;BS=0.20;PU=AGAAA;STR=-; chr1 3002526 CHG C . . . NS=1;DP=7;CTDP=7;CD=1;BS=0.1429;PU=TTTTCTT;STR=+; chr1 3002528 CHG C . . . NS=1;DP=4;CTDP=4;CD=0;BS=0;PU=AAAA;STR=-; chr1 3002529 CHH C . . . NS=1;DP=7;CTDP=7;CD=0;BS=0;PU=TTTTTTT;STR=+; chr1 3002530 CHH C C . . NS=1;DP=7;CTDP=7;CD=2;BS=0.2857;PU=TTTTCTC;STR=+;
-
<sample-name>_<reference-name>.<bed-file-name>.METHYLATEDregions.txt. Summary of methylation levels per annotated region and context, for Watson and Crick strands, and globally. The methylation level of a particular region is reported as weighted mean of cytosine methylation (WMCM). This information is provided for each methylation context (CG, CHG and CHH). Columns are:
- Region name
- m[CG|CHG|CHH] [WATSON|CRICK]. Number of methylated reads at [CG|CHG|CHH] context in the [WATSON|CRICK] strand inside the region
- depth[CG|CHG|CHH] [WATSON|CRICK]. Number of reads at [CG|CHG|CHH] context in the [WATSON|CRICK] strand inside the region
- WMCM [CG|CHG|CHH] [WATSON|CRICK]. Methylation level (given as WMCM) of the region only considering cytosines in [CG|CHG|CHH] context in the [WATSON|CRICK] strand
- m[CG|CHG|CHH] total methylation. Number of methylated reads at [CG|CHG|CHH] context inside the region
- m[CG|CHG|CHH] total depth. Number of reads at [CG|CHG|CHH] context inside the region
- WMCM [CG|CHG|CHH] total. Methylation level (given as WMCM) of the region and in [CG|CHG|CHH] context
#Region mCG WATSON depthCG WATSON WMCM CG WATSON mCG CRICK depthCG CRICK WMCM CG CRICK mCG total methylation mCG total depth WMCM CG TOTAL mCHG WATSON depthCHG WATSON WMCM CHG WATSON mCHG CRICK depthCHG CRICK WMCM CHG CRICK mCHG total methylation mCHG total depth WMCM CHG TOTAL mCHH WATSON depthCHH WATSON WMCM CHH WATSON mCHH CRICK depthCHH CRICK WMCM CHH CRICK mCHH total methylation mCHH total depth WMCM CHH TOTAL IRS1 326 825 0.3951515 0 0 � 326 825 0.3951515 55 3014 0.0182482 0 0 � 55 3014 0.0182482 65 3608 0.0180155 0 0 � 65 3608 0.0180155 CDKN1A 184466 258643 0.713207 0 0 � 184466 258643 0.713207 47922 1601963 0.0299145 0 0 � 47922 1601963 0.0299145 116802 3473706 0.0336246 0 0 � 116802 3473706 0.0336246 PDE7B 119657 962016 0.1243815 0 0 � 119657 962016 0.1243815 99826 5767612 0.017308 0 0 � 99826 5767612 0.017308 130743 8961569 0.0145893 0 0 � 130743 8961569 0.0145893 INS 80460 482701 0.166687 0 0 � 80460 482701 0.166687 47126 2413536 0.0195257 0 0 � 47126 2413536 0.0195257 81389 4584905 0.0177515 0 0 � 81389 4584905 0.0177515 MEG3 960649 2264207 0.4242761 0 0 � 960649 2264207 0.4242761 44603 2861193 0.015589 0 0 � 44603 2861193 0.015589 95019 6310408 0.0150575 0 0 � 95019 6310408 0.0150575
2.1.6 analyze-differential-methylation (bicycle >1.5)
usage: bicycle analyze-differential-methylation -p <project-directory> -t <treatment-samples> -c <control-samples> [-x <context>] [-b <region-beds>]
--project-directory/-p
project directory. Use command create-project to create a new project
--treatment-samples/-t
Comma-separated (with no spaces) list of sample names belonging to 'treatment' group
--control-samples/-c
Comma-separated (with no spaces) list of sample names belonging to 'control' group
--context/-x
Comma-separated (with no spaces) list of CpG contexts to analyze: CG, CHG or CHH. For example: CG,CHG (default: CG)
--region-beds/-b
Comma-separated (with no spaces) list of BED files to analyze at region-level
Input files
- A bicycle project directory.
Output files
-
<reference-name>_<control-samples>__VS___<treatment-samples>.DMC.tsv. Differential methylation for
each cytosine (DMC) if two different conditions were compared or tested for differential methylation. For each cytosine, the following information is written: chromosome and cytosine position, methylation context, cytosine methylation for each sample (replicate) of the treatment condition and for each sample (replicate) of the control condition, methylation average for each condition, fold-change of treatment/control methylation in log2, p-value and q-value (corrected p-value).
#SEQ POS CONTEXT SRR2052492 (treatment) SRR2052493 (treatment) SRR2052494 (treatment) SRR2052495 (treatment) SRR2052496 (treatment) SRR2052487 (control) SRR2052488 (control) SRR2052489 (control) SRR2052490 (control) SRR2052491 (control) treatment average control average log2FC(treament/control) p-value q-value chr2 227659636 CG 149/391 164/391 175/532 59/224 241/545 127/215 110/268 157/350 184/415 217/543 0.3783005280844935 0.4438860971524288 -0.23065673277002718 0.05841941645729131 0.1674212539388247 chr2 227659700 CG 166/452 127/451 222/595 87/254 76/605 89/241 89/312 142/393 231/476 132/612 0.2876537971998303 0.3357915437561455 -0.22323238454641373 0.4278506944611703 0.8414396991069683 chr2 227659733 CG 96/452 63/441 47/586 43/255 123/594 53/241 57/311 81/390 156/471 112/607 0.1597938144329897 0.2272277227722772 -0.5079272975749031 0.07887112467158257 0.2062856828272065 chr2 227659773 CG 60/230 139/227 112/302 51/128 94/303 57/121 69/154 75/203 109/238 146/308 0.3831932773109244 0.4453125 -0.21674585819530579 0.3448729257458535 0.7016380213450122 chr6 36645500 CG 27673/42629 21430/27350 14137/28027 18233/28767 17312/20791 53593/64866 38209/46606 42481/53462 27962/35198 28287/38770 0.6694383453958961 0.7975320424274389 -0.2525912922759481 0.08740918763864683 0.2062856828272065 chr6 36645608 CG 59023/84460 36772/54145 17238/55554 37511/56962 30500/41182 91285/128578 70279/92203 83695/105815 46176/69728 49798/76706 0.619370995165975 0.7213770796778217 -0.21994976118069076 0.22179296224732525 0.46734945616400675
-
<reference-name>_<control-samples>__VS___<treatment-samples>.<bed-file-name>.DMR.tsv. Differential methylation for each annotated region that was provided. The information written here is similar to the one written in *.DMC.tsv, but in genomic region level.
#region sequence start stop SRR2052492 (treatment) SRR2052493 (treatment) SRR2052494 (treatment) SRR2052495 (treatment) SRR2052496 (treatment) SRR2052487 (control) SRR2052488 (control) SRR2052489 (control) SRR2052490 (control) SRR2052491 (control) treatment average control average log2FC(treament/control) p-value q-value MEG3 chr14 101291953 101292257 1455768/2043201 1636631/3258147 1497615/2643988 1278819/2677687 1699837/1958100 960649/2260743 1655354/3623531 1234101/2867390 1729232/3490690 2112253/4771083 0.6015893811705044 0.45208907524094044 0.4121720465419593 0.032485239405786 0.054142065676310004 CDKN1A chr6 36645463 36645696 106164/169351 67574/108667 39848/111440 70332/114278 56000/82614 184466/257701 135047/184961 153820/212228 90107/139840 97084/153940 0.5797185981069327 0.6962631895179566 -0.264279982267956 0.06970890125229327 0.0871361265653666 IRS1 chr2 227659612 227659781 471/1525 493/1510 556/2015 240/861 534/2047 326/818 325/1045 455/1336 680/1600 607/2070 0.2882633827594873 0.34837676517688165 -0.27326082007437236 0.031291095111098274 0.054142065676310004 INS chr11 2182552 2182775 133094/209138 291969/567402 119026/425194 152310/651761 177366/278973 80460/481158 165062/765934 174273/633564 169227/724203 288122/1036615 0.40974354597583645 0.2408760847942344 0.7664300613080263 0.022056895484407948 0.054142065676310004 PDE7B chr6 136172766 136172917 358560/2258785 151970/1578967 368147/2086541 104049/1062921 506169/2399992 119657/960632 197487/1205221 168450/1002387 197266/1376956 112174/1444852 0.15860896202767896 0.1327258145510687 0.2570252958195374 0.6929437289294518 0.6929437289294518
3. FAQ
3.1 Increase the memory RAM that bicycle uses
In order to increase the memory RAM that bicycle can use, you just need to set the -Xmx parameter before the bicycle command. For instance, to set a maximum RAM memory of 16G:
bicycle -Xmx16G align -p data/myproject -t 4
3.2 Working with multiple data directories in bicycle
Sometimes it is desirable to work with data which is located in different directories. For instance, you may have your reference genome at /data/genomes/my_genome and your samples at ~/bisulfite/reads/my_project_reads. When using bicycle as a regular program, this may be easily achieved using different directories or even using symbolic links. However, it seem that symbolic links do not work properly in Docker so you may need to mount different directories when running the Docker image as the following example shows:
LOCAL_PROJECT_DIR="~/bicycle_projects/my_bicycle_project"
LOCAL_REFERENCE_GENOME="/data/genomes/my_genome"
LOCAL_SAMPLES_DIR="~/bisulfite/reads/my_project_reads"
REFERENCE_GENOME="genome"
SAMPLES_DIR="samples"
PROJECT_DIR="data"
$BICYCLE="docker run -v $LOCAL_PROJECT_DIR:/$PROJECT_DIR -v $LOCAL_SAMPLES_DIR:/$SAMPLES_DIR -v $LOCAL_REFERENCE_GENOME:/$REFERENCE_GENOME -u `id -u \`whoami\`` -it singgroup/bicycle bicycle"
$BICYCLE create-project -p $PROJECT_DIR -r $REFERENCE_GENOME -f $SAMPLES_DIR --paired-mate1-regexp _1.fastq