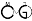 bicycle
bicycle
How it works?
When DNA is treated with sodium bisulfite, unmethylated cytosines are converted to thymines. This basic property is where the analysis workflow relies on.
Once DNA has been treated with sodium bisulfite and sequenced with high-throuhgput technologies, millions of reads are produced. Reads then have to be aligned to a reference genome in order to study methylation levels.
However, it is not possible to initially align those reads to a reference genome, since all unmethylated cytosines have been converted to thymines, leading to many mismatches in the alignment. To overcome this, both the reference genome sequence and the read sequences are bisulfited in-silico, by simply replacing all cytosines with thymines.
This procedure allows to align reads to the reference genome, but only the reads of the Watson (or positive) strand. The bisulfited reads of the opposite strand are no longer reverse-complementary of the Watson strand. So it is neccessary to create an additional reference genome (the Crick ref. genome), by replacing Guanines with Adenines. Reads coming from the negative strand align to the Crick genome. In consequence, we have to align all reads to both reference genomes, where a read is expected to align to one of both genomes.
After the alignment step, in-silico bisulfited reads are replaced with the original ones (where only the unmethylated cytosines were replaced).
Criteria for read methylation:
- At every reference cytosine, each read aligned to the Watson bisulfited ref. containing a cytosine is considered to be methylated. In case that there is a thymine, the read is considered to be unmethylated in that position.
- At every reference guanine (cytosine in the negative strand), each read aligned to the Crick bisulfited ref. containing a guanine is considered to be methylated. In case that there is an adenine, the read is considered to be unmethylated in that position.
Finally, a methylcytosine calling step is applied. At each reference cytosine and given the number of methylated vs. unmethylated reads, that is, its methylation level, a statistical test is applied to assess if this methylation level can be due to real methylation or due to error (bisulfite conversion error plus sequencing/alignment error).
bicycle pipeline
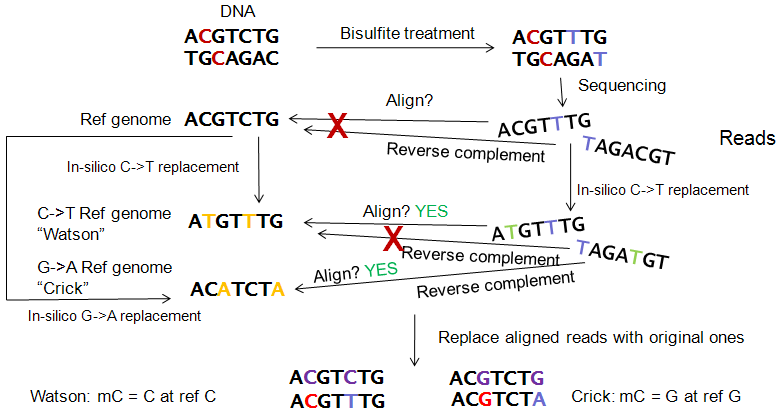
bicycle is based on 6 main commands, where the temporal data and results are stored in a project. The commands are:
- Create project. A project is simply a new directory with a configuration file poiting to the references, reads, samtools and bowtie directories.
- Reference bisulfitation. Creation of the bisulfited references (both Watson and Crick). By default, the generated references are placed in the references directory, in order to reuse this reference in several methylation projects.
- Reference index. Build bowtie indexes of the bisulfited references. As before, the generated indexes are placed in the references directory.
- Align. Align all bisulfited reads against the bisulfited references and place the alignments in the "output" subdirectory of the project.
- Analyze methylation. Methylation level analysis and methylcytosines calling.
- Analyze differential methylation. Differential methylation analysis.